
Introduction
With the advancement of automotive technology, TPMS systems have become increasingly sophisticated. However, when it comes to TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation, vehicle owners and technicians often ask one question: Do TPMS sensors need to be distinguished by front/rear or left/right positions? This article answers this question and delves into the installation, calibration processes, and common issues in practical operations.
How TPMS Sensors Work
TPMS relies on sensors to monitor tire pressure in real-time and wirelessly transmits data to the vehicle’s central computer system. There are two main types of TPMS:
- Direct TPMS:
Each wheel is equipped with an individual sensor that directly measures tire pressure. These sensors are typically mounted on the valve stem or inside the wheel rim and transmit data via radio frequencies (e.g., 315 MHz or 433 MHz, depending on regional standards) to the vehicle’s receiver module. - Indirect TPMS:
This system uses wheel speed sensors (part of the ABS) to estimate pressure based on rotational differences. It doesn’t use physical pressure sensors, and its accuracy is lower. Since this article mainly focuses on TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation, we will not delve deeper into indirect systems.
Installing and TPMS Sensor Position Differentiation

Before Installation
Before installation, a new TPMS sensor does not have a specific front/rear position designation. It can be installed in any wheel position. At this stage, the sensor’s functionality is not dependent on the wheel position.
After Installation
Once the sensor is installed and paired with the vehicle’s TPMS system, the system must recognize each sensor’s specific position (front-left, front-right, rear-left, rear-right) to ensure the tire pressure monitoring system can display the correct data.
- Automatic Position Recognition:
Most modern vehicles are equipped with systems that automatically detect sensor positions. Using advanced algorithms or additional hardware (such as accelerometers), the system can automatically recognize sensor positions after driving a short distance (usually 25-40 km/h for 5-10 minutes). - Manual Registration:
For older or special models, the vehicle owner or technician must use a dedicated TPMS tool to trigger each sensor in a specific order (e.g., clockwise: left-front → right-front → right-rear → left-rear). The system will assign IDs to each sensor based on the trigger order.
When replacing the sensor, ensure that it matches the original vehicle model (such as frequency, part number, etc.). You can choose the OEM TPMS sensor to ensure proper matching.
The Importance of TPMS Sensor Front Rear Position Differentiation
Correct TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation is crucial for vehicle safety and accurate tire monitoring. If sensors are not properly assigned to their respective positions, the system may display incorrect tire pressure readings. This can lead to confusion when a TPMS warning light appears, making it difficult to identify which tire or sensor is malfunctioning. Accurate position differentiation ensures that each wheel’s pressure is monitored correctly, allows for timely alerts of potential issues, and helps maintain optimal vehicle performance and safety.
Calibration and Re-learning Procedures
For Vehicles with Automatic Position Recognition

- Drive Activation:
Drive the vehicle at over 25 km/h on a straight road for 5-10 minutes, allowing the system to automatically recognize the sensor positions. - System Reset:
If automatic recognition fails, reset the system via the infotainment menu by selecting “TPMS Reset” or “Relearn” option. - Verification:
Check the display inside the vehicle to confirm whether the tire pressure readings for each wheel position are correct.
For Vehicles Requiring Manual Calibration
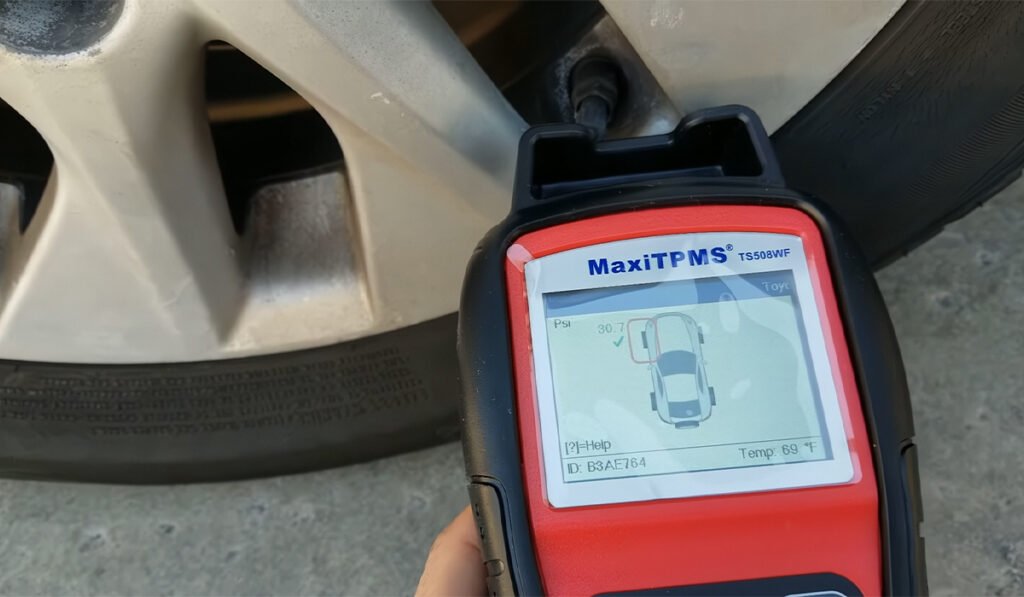

- Tool Preparation:
Use a dedicated TPMS tool (e.g., JDiag TPMS Master) to trigger each sensor. - Activation Sequence:
Follow the vehicle’s manual instructions to trigger the sensors in a specific order, usually clockwise: left-front → right-front → right-rear → left-rear. - OBD Learning:
Connect the OBD tool to the vehicle and wait for the OBD system to learn the sensor positions. - Observation:
Check the instrument panel to confirm whether the warning light disappears and the tire pressure values are correctly displayed.
Various Vehicle Models Re-matching Method
If you need to check specific matching methods for different vehicle models, you can refer to the table below:
View TPMS sensor matching method for different vehicle models
This table lists detailed sensor matching steps for different brands and models, allowing technicians and vehicle owners to quickly reference the process.
Common Application Issues and Solutions

- TPMS Warning Light Stays On
This is often caused by unregistered sensors, low sensor battery, or the sensor not being matched to the system. Vehicle owners can use diagnostic tools to check the sensor status and recalibrate or replace faulty sensors. - Sensor Signal Interference
Metallic wheel coatings or aftermarket accessories (such as tire decoration strips) may interfere with the sensor signal. Ensure that sensors are correctly installed and avoid using accessories that may block the signal. - Normal Tire Pressure but TPMS Light On
This is usually caused by an error in TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation,which can be corrected by recalibrating the sensor. It can be manually calibrated, or you can drive for a while, allowing the system to re-recognize and correct the position.
Global TPMS Regulatory Standards
Understanding regional requirements is crucial for the correct TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation:
- United States (FMVSS 138):
Since 2007, all new vehicles must be equipped with TPMS and have position-specific monitoring and alert systems. - Europe (ECE R64):
Since 2014, all new vehicles must be equipped with TPMS, with strict position accuracy requirements. - China (GB 26149):
Implemented in 2020, following European standards with specific sensor position monitoring rules.
Future Technology Trends
- Bluetooth Sensor Popularity
With the advancement of technology, Bluetooth sensors are gradually replacing RF technology, becoming the mainstream choice for future TPMS due to their lower power consumption and better compatibility. - Direct TPMS Sensor Popularity
Direct TPMS sensors will continue to replace indirect systems, providing higher accuracy and real-time monitoring. - RF Sensors Gradually Reducing
As Bluetooth technology becomes more popular, the use of RF TPMS sensors will gradually decline, especially in high-end smart vehicles.
Note: Regardless of whether Bluetooth sensors are installed before or after, TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation is not necessary, as they automatically calibrate.
Conclusion
Proper TPMS sensor front rear position differentiation is crucial for vehicle safety and performance. While sensors do not have specific position requirements during installation, correct registration and calibration ensure accurate monitoring. Modern vehicles typically feature automatic matching functionality, while older models require manual calibration. Understanding these procedures ensures optimal TPMS system performance and safety.
As TPMS technology evolves, it will become more integrated, providing enhanced accuracy and improving tire management. If you want to ensure your vehicle is equipped with high-quality sensors, check out our tire pressure sensors for reliable performance and compatibility.
